I have a set of csv file pairs called e.g.
1111_AB.csv
1111_AB_type47.csv
1112_AB.csv
1112_AB_type47.csv
I need to manipulate the contents of the *_type47 files and then append them, minus the header line, to the foot of the master file.
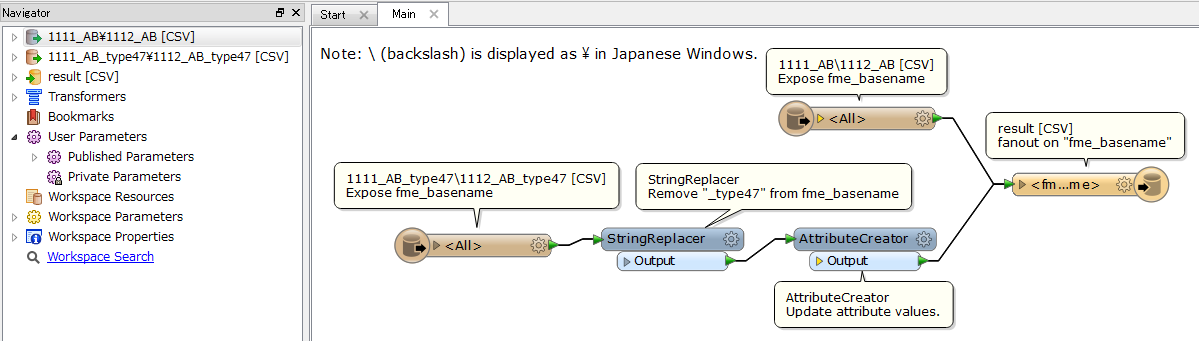
In my workspace I've got a CSV reader --> FeatureTypeExtractor (to write the file name to an attribute) --> StringReplacer (to replace the _type47.csv with an empty string) --> AttributeCreator (to update the value of an attribute for each feature from 47 to 52).
Once updated I'd like to write the features to the foot of the master CSV files (based on the value in my FeatureTypeExtractor) in EXACTLY the same order and format as the source.
What's the best strategy for this? I'm a bit stuck...
Thanks,
Matt