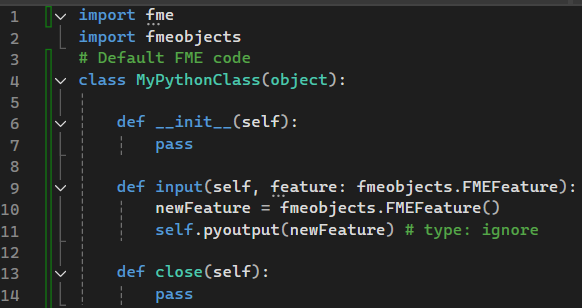
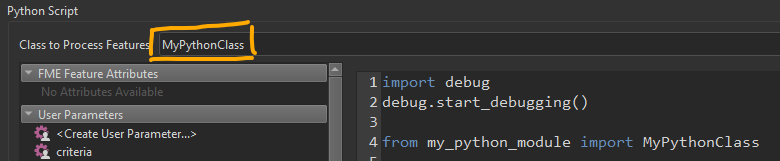
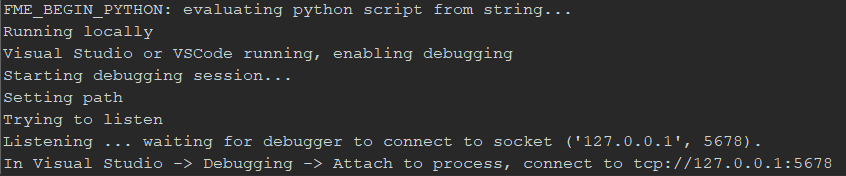
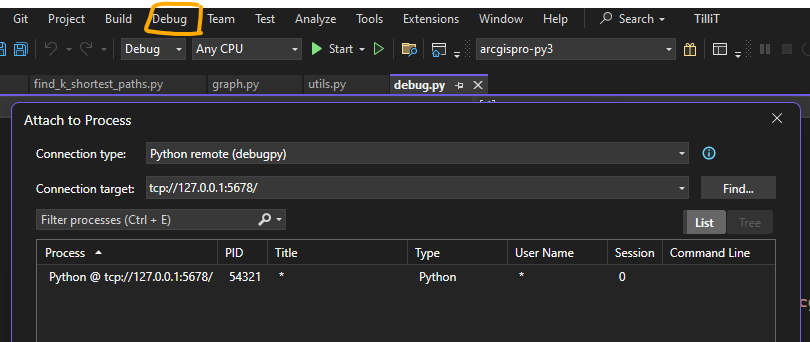
In a process in my company we use a Python script (PythonCaller) to call a download API, we need to modify it, but we get some errors that I don't get when running the script from Python on the Windows command line.
Is there a way to debug the execution of the script in FME?