In FME what is the diffrence between composite-surface and multi-surface? As far as I can tell when reading the description they do pretty much the same thing. How do they diffrientiate and why would I use one rather then another?
Solved
What's the difference between multi-surface and composite surface?
Best answer by takashi
Hi @hadhafang, in my understanding, those two geometry types are different in not only internal data structure (IFMECompositeSurface and IFMEMultiSurface) also the object to represent conceptually. That is, a composite surface is a geometry that represents a continuous surface of a single object, a multi-surface is an aggregate that represents surfaces (regardless of whether those are continuous or not) of one or more objects.
For example, the surface for each individual box can be represented by either a composite surface or a multi-surface (both consisting of six Faces), but an aggregate of the surfaces of the two boxes should be represented by a multi-surface (or an aggregate), conceptually.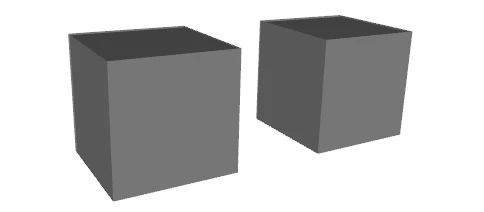
This post is closed to further activity.
It may be an old question, an answered question, an implemented idea, or a notification-only post.
Please check post dates before relying on any information in a question or answer.
For follow-up or related questions, please post a new question or idea.
If there is a genuine update to be made, please contact us and request that the post is reopened.
It may be an old question, an answered question, an implemented idea, or a notification-only post.
Please check post dates before relying on any information in a question or answer.
For follow-up or related questions, please post a new question or idea.
If there is a genuine update to be made, please contact us and request that the post is reopened.