Hello everyone,
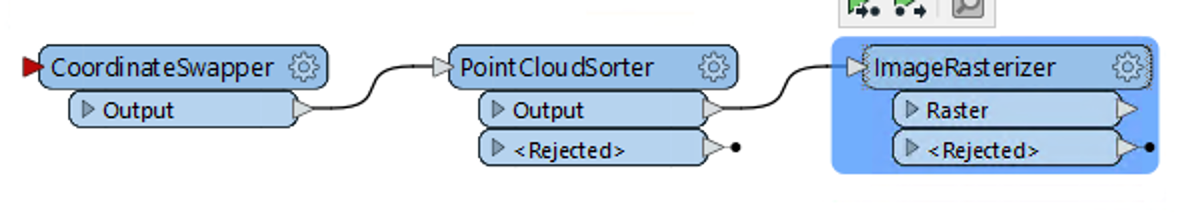
I have a point cloud of a section of a road, and I'm wondering if i can get a front view picture of the point cloud like in the screenshot using FME. I also have the axe of the road if it can help with the direction.
Thank you in advance.