We're currently integrating FME with Databricks. In a vanilla Databricks environment, everything works as expected—both reading from and writing to Unity Catalog tables using the Databricks Reader and Writer in FME.
However, in our organizational Databricks environment, we're encountering an issue:
-
Reading works fine using the same credentials (tested with both OAuth and PAT).
-
Writing, however, gets stuck in an infinite polling loop in FME, with no error message returned.
The same credentials and target table work fine for writing when using a Python script in the same environment, so it seems to be specific to how FME writes data.
Given that writing works in the vanilla setup but not in our organizational environment, I suspect the issue is related to permissions or Unity Catalog access controls that are more tightly restricted in the corporate setup.
My questions:
-
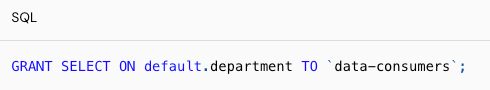
What exact permissions are required in Databricks for FME's Databricks Writer to write to Unity Catalog tables?
-
What method does FME use under the hood to perform write operations to Databricks/Unity Catalog
Environment details:
-
FME version: 2024.2.2
-
Platform: Azure Databricks
-
Authentication: Both OAuth and PAT tested
-
Target: Unity Catalog tables
Thanks for any guidance or insight you can provide!
Best regards,
Marco