FME 2025.0 is here, packed with exciting new features that transform how you work with data. Our new stream capabilities improve real-time processing by introducing Remote and Heartbeat support, turning fast-moving data into immediate insights for smarter decision-making. Native Neo4J integration simplifies complex graph analytics, while centralized Connection Storage in FME Flow streamlines shared connection management. With 2025.0, data handling is more agile, flexible, and powerful than ever before.
Stay tuned for big groundbreaking advancements reveals at The Peak of Data and AI.
Feature Highlights
Remote Streams: FME Flow Streams can now run on Remote Engines Services, as Remote Streams, to run streams closer to data sources, drastically reducing latency and boosting scalability. To maintain stability, Remote Streams automatically shut down after 24 hours of disconnection from the Remote Engines Service, and seamlessly resume when reconnected—all supported by an improved connection UI for a smoother setup experience.
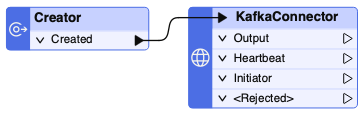
Heartbeat Streams: Our new Heartbeat support ensures that when streams experience extended quiet periods, the TimeWindower now processes features accurately, avoiding outdated data retention. This feature introduces a configurable heartbeat option on the connector, enabling the system to stay responsive even in the absence of data flow. KafkaConnector is the first to support this capability, with additional streaming connectors scheduled to release in the coming months.
Want to learn more about this feature? Watch our short demo video here.
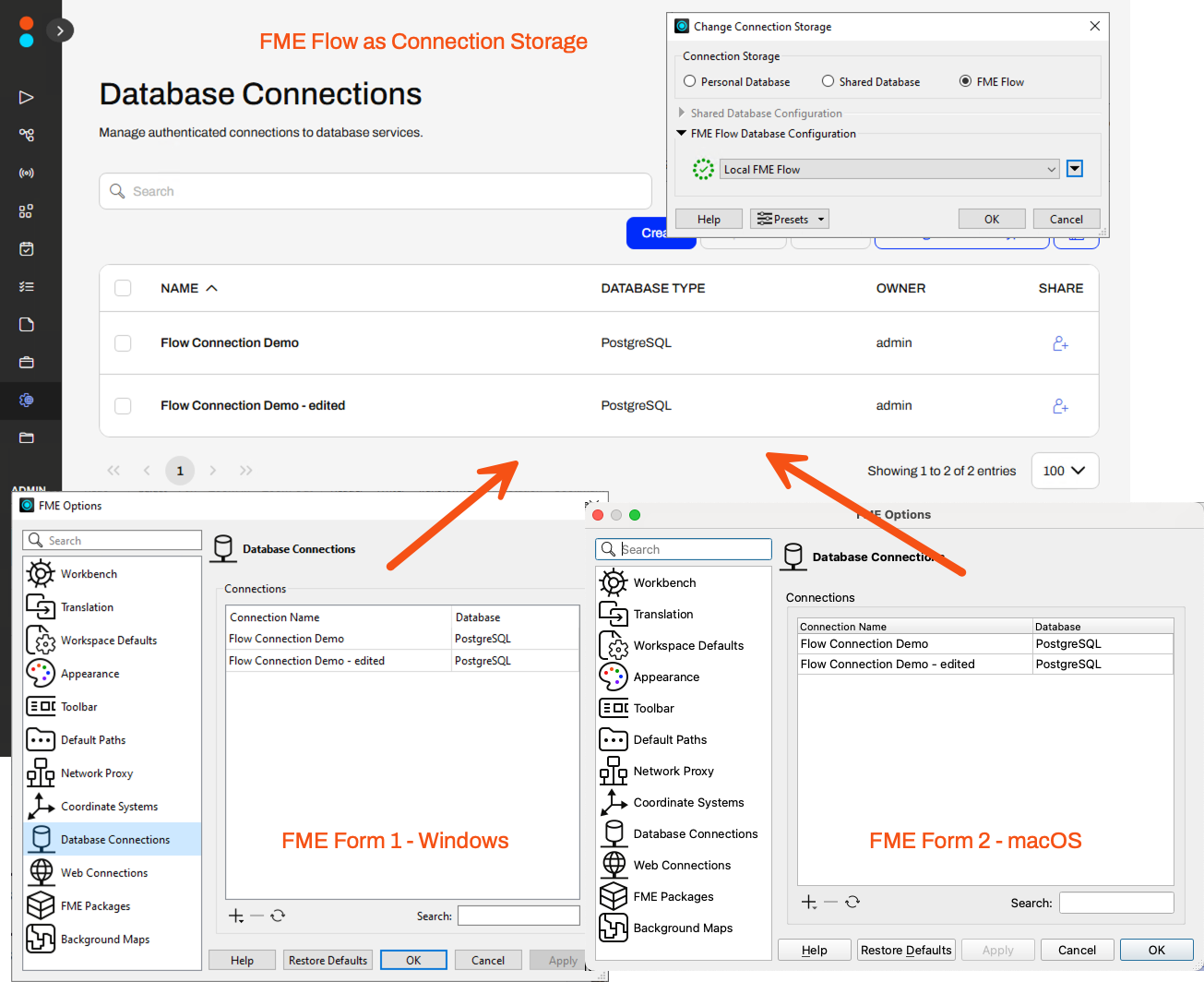
FME Flow as Connection Storage Location: Streamline your connection management by leveraging FME Flow as a centralized repository for database and web connections. By designating FME Flow as your storage location in FME Form, teams gain immediate access to shared connections without extra setup. We’ve ensured that a Centralized Connection store enables consistent configurations, tightens access controls, and improves overall workflow efficiency.
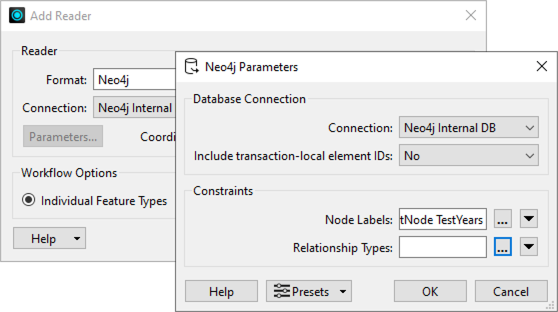
Neo4j Reader: FME now includes native support for Neo4j, enabling users to effortlessly integrate graph database queries into their workflows. The Neo4j Reader lets users execute Cypher queries directly to retrieve nodes, relationships, and paths, all while preserving the integrity of your graph structures. With the added flexibility of SQL transformers to refine query results, users can now more easily analyze network relationships, connected assets, or social graphs.
Additional Enhancements
Spatial Definition Table — Improving Spatial Data Visibility: The new Spatial Definition Table within Reader Feature Types displays spatial column names, geometry types, and spatial types (where applicable) to enhance spatial data discovery. Additionally, enhanced canvas objects now indicate the presence of spatial data by showing the spatial column name when available, complementing the Schema Preview window for a more intuitive and efficient data exploration experience.
User Parameters — Precise Conditional Visibility Control: Building on the Conditional Visibility feature from FME 2023.0, FME 2025.0 now introduces Compound Conditions. This enhancement allows for multiple conditional statements and provides a broader set of operators, offering even more control over when parameters appear for an intuitive user interface.
Want to learn more about this feature? Watch our short demo video here.
New and Updated Integrations
IBMMQConnector: FME now includes a dedicated IBMMQConnector for IBM MQ 9.X, streamlining both sending and receiving messages. Delivered as an FME package, the connector eliminates the need for complex JMS library setups, offering simplified connection parameters and supporting both streaming and batch message processing.
RabbitMQConnector Quorum Queue Support: In addition to classic queues, the RabbitMQConnector now supports quorum and stream queues. With the new Queue Type parameter, users can select Classic, Quorum, or Stream, facilitating reliable and flexible message retrieval across all RabbitMQ queue types.
Database Case Control — Table and Column Names: FME now offers enhanced control for managing table and column name formatting across all database formats. Users can choose to convert names to uppercase, lowercase, or keep the original case while ensuring compatibility across different database systems.
Databases — Write Schema-Only Tables: With the new Always Create Table setting available across all major database formats, FME generates database tables even when no feature data is provided. This streamlines schema-only migrations, allowing users to replicate database structures from source to destination without requiring data.
Want to learn more about this feature? Watch our short demo video here.
Simplified Database Integrations — Unified Format for Spatial and Non-Spatial Data: FME has consolidated major JDBC-based database formats to support both spatial and non-spatial tables under one unified format name.
Improved formats:
- Snowflake
- Microsoft SQL Server (JDBC)
- Microsoft Azure SQL Database (JDBC)
- SAP HANA and SAP HANA Cloud
- Teradata
Stay tuned for further database unification in further releases.
Add IFC Opening Feature Reading: FME’s IFC API Reader now supports IfcOpeningElement features, allowing for more precise handling of wall, window, and door openings. This update enables accurate clipping of boundary surfaces so that walls, doors, and windows are rendered as single flat surfaces when necessary. By using IfcOpeningElement solids for geometry processing, interoperability across BIM, GIS, and 3D modeling applications has been significantly improved.